
The KEGG Pathways database
The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) is a collection of databases and resources for studying high-level functions and utilities of the biological systems [Kanehisa et al. 2000, Kanehisa et al. 2014]. The KEGG database project started in 1995 at the Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, looking for a computerized representation for the linkages between genomic information and higher-level systemic functions of the cell, the organism and the ecosystem (Figure 1).
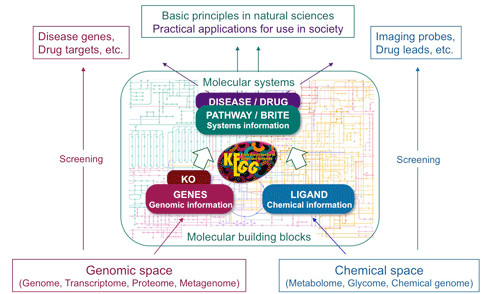
Figure 1: Overview for the integrated information in KEGG Database.
Last release of KEGG database (Release 76.0, October 1, 2015) includes 17 main databases maintained in the internal Oracle database [20, 21], which contain wide genomic and molecular-level information for up to 4000 species (313 eukaryotes, 3507 bacteria and 215 archaea). These databases are broadly categorized into systems information, genomic information, chemical information and health information (Table 1)
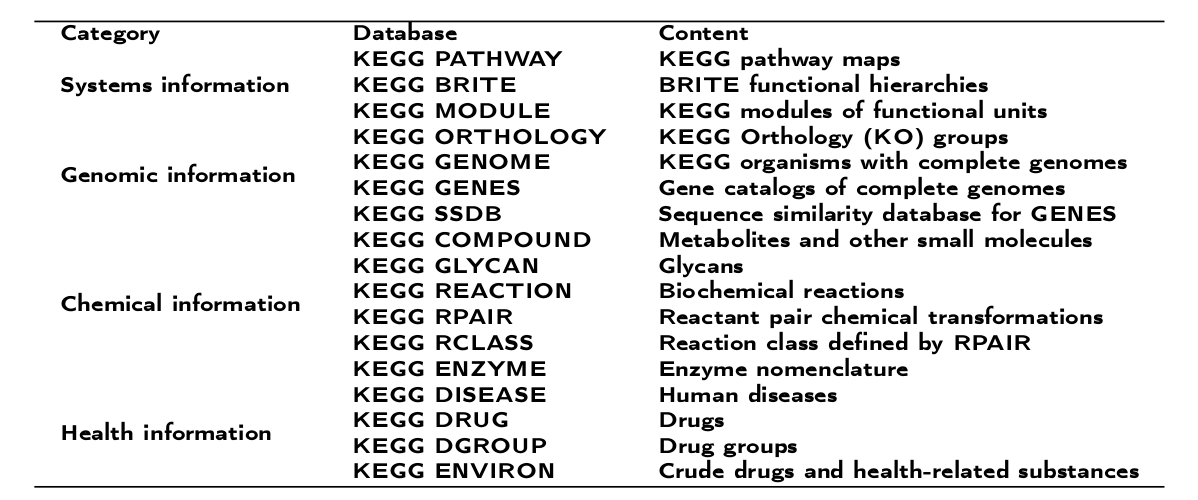
Table 1: Main categories for KEGG databases.
The KEGG PATHWAY database is a collection of graphical diagrams, usually known as pathway maps, that represent molecular interaction and reaction networks within a cell during specific biochemical processes, which usually leads into a product or change in the cell. KEGG PATHWAY contains about 478 reference pathways (Release 76.0, October 1, 2015), which are manually drawn and continuously updated according to biochemical evidences; that are categorized by the hierarchical classification of Figure 2. In addition to reference maps, KEGG PATHWAY contains over than 400,000 organism-specific pathways inferred by automatic mapping based on existing orthology events between species.
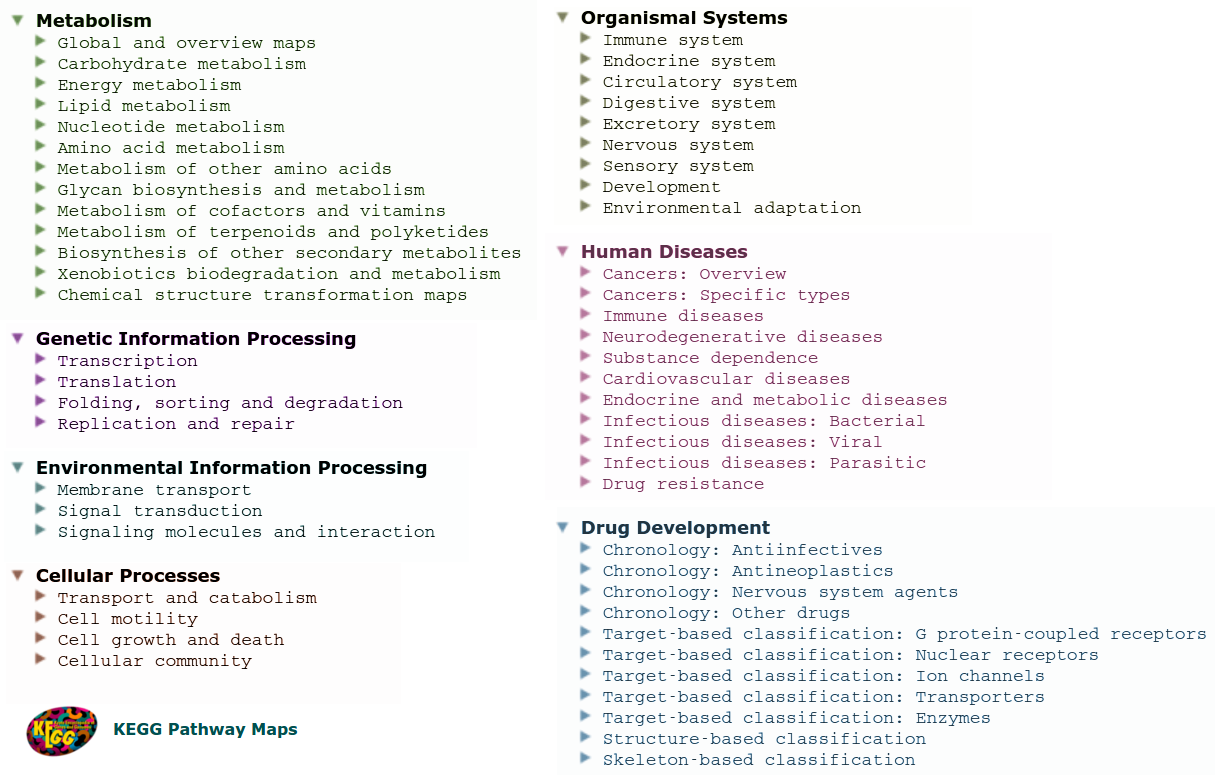
Figure 2: Hierarchical classification for KEGG Pathways: main and secondary categories.
Each pathway in KEGG is identified by a 5 digit number (entry name or the accession number) preceded by a 2-4 letter code that indicates the organism or databases. Some examples for valid identifiers are map03060 (Reference Protein export pathway, Figure 3), mmu03060 (Mus Musculus Protein export pathway) or hsa03060 (Homo Sapiens Protein export pathway).
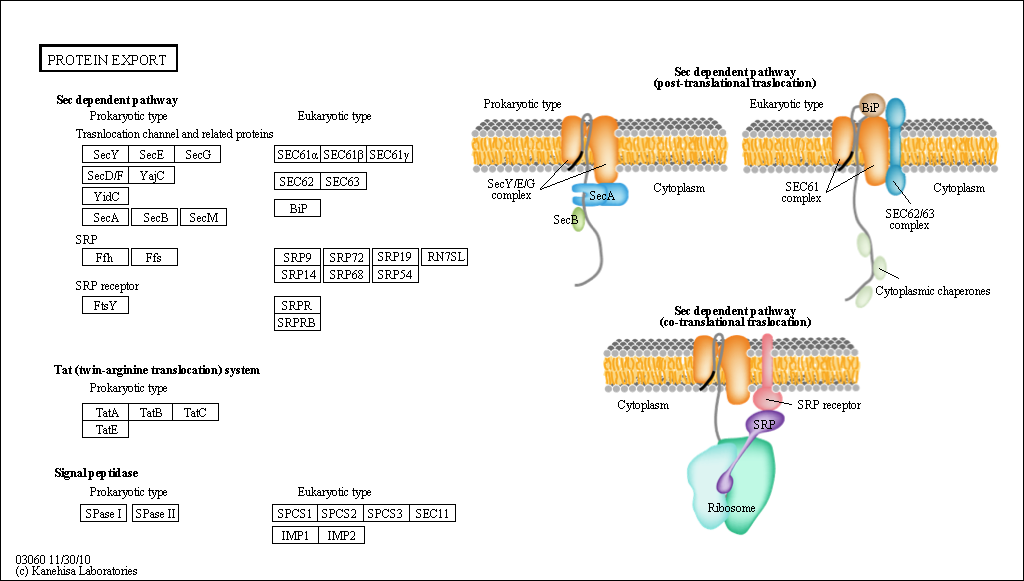
Figure 3: KEGG diagram for Reference Protein export pathway (KEGG ID map03060).
Pathways are manually drawn using an in-house software named KegSketch using different graphics resources to visualize the information. For example, boxes represent gene products, mostly proteins but also RNA, while circles represent other molecules such as chemical compounds (Figure 4a). Interactions between biomolecules or other pathways are drawn using different arrows (Figure 4b); and the combination of multiple shapes can be interpreted as different biochemical processes or molecular interactions (Figure 4c). Coloring is also another resource for diagram interpretation: as general rule reference pathways are not colored while the variations of pathways for KEGG ENZYME (EC) database are colored blue, and organism-specific pathways are colored green, where coloring indicates that the biological entity (i.e gene or compound) exist in the corresponding database (Figure 4d).
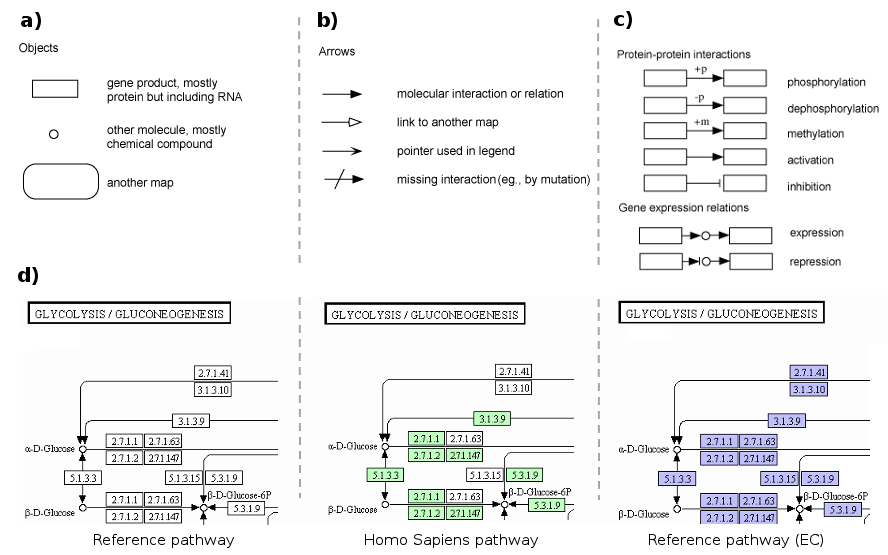
Figure 4: Some examples for the graphics resources uses for KEGG diagram to visualize the information.
Finally, it is interesting to highlight the existence of an exchange format for the KEGG pathway maps known as KEGG Markup Language (KGML), which contain computer- ized information about graphical objects and their relations in the KEGG pathway, i.e. coordinates for shapes, dimensions, colors or links to databases, among others (Code fragment 1).
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE pathway SYSTEM "http://www.kegg.jp/kegg/xml/KGML_v0.7.1_.dtd">
<pathway name="path:hsa00010" org="hsa" title="Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis" image="http://www.kegg.jp/.../hsa00010.png" link="...">
<entry id="13" name="hsa:226 hsa:229 hsa:230" type="gene" reaction="rn:R01070" link="...">
<graphics type="rectangle" x="483" y="407" width="46" height="17" name="ALDOA, ALDA, GSD12,..." fgcolor="#000" bgcolor="..." />
</entry>
<entry id="37" name="hsa:217 hsa:219 hsa:223 hsa:224 hsa:501" type="gene" reaction="rn:R00710">
[...]
</entry>
[...]
<entry id="113" name="cpd:C00036" type="compound"
link="http://www.kegg.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?C00036">
<graphics name="C00036" fgcolor="#000000" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" type="circle" x="146" y="736" width="8" height="8"/>
</entry>
[...]
<relation entry1="68" entry2="70" type="ECrel">
<subtype name="compound" value="86"/>
</relation>
[...]
<reaction id="47" name="rn:R00014" type="irreversible">
<substrate id="98" name="cpd:C00022"/>
<substrate id="136" name="cpd:C00068"/>
<product id="99" name="cpd:C05125"/>
</reaction>
[...]
</pathway>
Code fragment 1: Fragment for the KGML file for KEGG Pathway Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis for Homo Sapiens.